Compression Fracture
A vertabral compression fracture is a form of fracture that 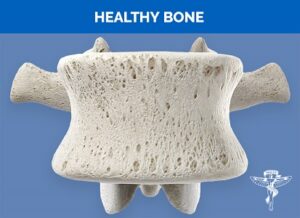 occurs when the vertebral body of the spine collapses or compresses. It is also referred to as a wedge fracture, vertebral fracture, or osteoporotic fracture. The fracture is defined by the vertebral body shrinking or decreasing in height by at least 15 to 20% as a result of the fracture. They typically occur in osteoporotic bones. Compression Fractures can occur in all spinal segments but tend to be most frequent in the thoracic spine (upper back) and usually the lower part of that spinal region. By T10 to T12 and the upper segments of the lumbar spine L1. The fracture most commonly occurs in the front of the vertebrae leaving the posterior end of the vertebral body unchanged, providing a wedged-shaped bone. Thus the title”wedge fracture”
occurs when the vertebral body of the spine collapses or compresses. It is also referred to as a wedge fracture, vertebral fracture, or osteoporotic fracture. The fracture is defined by the vertebral body shrinking or decreasing in height by at least 15 to 20% as a result of the fracture. They typically occur in osteoporotic bones. Compression Fractures can occur in all spinal segments but tend to be most frequent in the thoracic spine (upper back) and usually the lower part of that spinal region. By T10 to T12 and the upper segments of the lumbar spine L1. The fracture most commonly occurs in the front of the vertebrae leaving the posterior end of the vertebral body unchanged, providing a wedged-shaped bone. Thus the title”wedge fracture”
Causes of compression fractures
The spine is supported by a complex system of articulating vertebrae, ribs, and other bones. As we age and approach the age of 60. Osteoporosis is likely to make the bones fragile and weak, so much so that simple everyday movements such as bending, twisting or a sudden cough or sneeze can compress spinal vertebrae leading to a fracture or crack.
Approximately eighty percent of people with osteoporosis-associated spinal compression fractures will experience intense acute localised back pain.
Easy movement such as walking or even standing will intensify the pain.
Reduction of height.
Difficulty breathing and decreased lung capacity.
Increased spinal curvature and a stooped posture.
Decreased range of spinal motion.
Ongoing symptoms
Most people who fracture a spinal vertebra clarify a sudden onset of back pain after a simple daily activity such as:
onset of back pain after a simple daily activity such as:
* bending- to pick an item off the ground.
* Lifting – picking up the grocery bag or opening a window.
Falling – sudden movements like slipping or missing a step that jars the spoon.
Advanced osteoporosis raises the likelihood of a fracture and might occur with very minor activity, such as coughing, sneezing, getting in and out of chairs or bathtubs, and even rolling over in bed.
Because the fracture can be found at the front of the backbone, it is usually stable and infrequently associated with spinal cord injury, However, if the strain is placed on the cable then tingling, numbness, and weakness may occur.
Vertebral compression fractures that happen because of osteoporosis are rather common. Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women is common. It has been estimated that 25% of osteoporotic women will suffer a spinal compression fracture.
Osteoporosis has a four times higher incidence in women than men and 25 percent of men with osteoporosis over the age of 50 will had a bone fracture in the spine or hip as a result of osteoporosis.
One of the problems associated with wedge fractures is that the individual believes it’s overall non-specific back pain, such as muscle strain or ongoing pain as part of the aging process. Consequently, two-thirds of those bony fractures that occur annually aren’t diagnosed and stay untreated.
The pain caused by a vertebral fracture usually lasts for about four to six weeks. The severe pain has solved and is now a chronic aching pain localised to where the fracture took place.
Infection may occur long after the bone has healed as a result of altered biomechanics. Adjacent muscles, bones, tendons, and ligaments become overloaded and take on more stress to compensate for the harm. Lack of action and muscle atrophy exacerbate the condition.
Can Chiropractic help with compound fractures?
The initial step in therapy is to diagnose the fracture and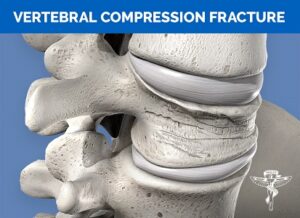 ascertain the spinal segment that’s fractured. X-ray imaging is imperative at this important stage. (Immediate Referral to a GP or specialist will be the initial step).
ascertain the spinal segment that’s fractured. X-ray imaging is imperative at this important stage. (Immediate Referral to a GP or specialist will be the initial step).
Compression Fracture
Stabilising the patient is the acute care and reducing stress to the spine so as healing can take place.
When the bone has healed chiropractors offer some level of therapy with trigger point therapy, decompression and gently treating surrounding structures that have been over-stressed and used because of protecting the fracture.
If you suspect you have a fracture call your GP or dial”000″ for instant help.
